
Similarly, a note receivable gives the holder, or the lender, the right to receive the amount from the borrower. Classification of Notes Receivables is critical for any business as it plays an essential role in managing finances efficiently while ensuring compliance with accounting standards. When notes are sold with conditions, the company creates contingent liability, and it is disclosed in the notes to financial statements. When the note’s maturity rises after the completion of 90 days, the interest amount is paid to MPC.
- With a promissory note, the third party who issued the note (called the maker) promises in writing, to pay an amount of money (principal and interest) to the business (called the payee) at a given time or on demand.
- This is because not all the sales made to a particular customer are recorded in the customer’s subsidiary accounts receivable ledger.
- Interest Revenue is credited because it is now earned, regardless of whether the company receives the cash.
- Notes receivable may not be suitable for every type of business since they tie up capital and may limit flexibility during times when liquidity becomes important.
- As interest on receivable is our income, it is recorded as (Debit interest receivable because we have not yet received the amount and credit interest revenue.
- The content on this website is provided “as is;” no representations are made that the content is error-free.
What Type of Account is Interest Income?
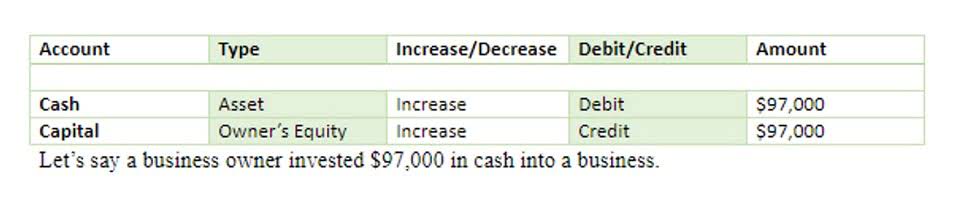
Since cash isn’t changing hands until later, we record the amount in the Interest Receivable account to keep track of what will be due. Their importance is underscored by their impact on liquidity and profitability, influencing how stakeholders view a firm’s financial health. Properly managing notes receivable is crucial for accurate financial statements and strategic decision-making. Notes receivable can be treated bookkeeping as either current assets or non-current assets depending on the timelines and intention of the company.
Journal Entries for Notes Receivable

To simplify the math, we will assume every month has 30 days and each year has 360 days. However, there are also some downsides to consider when dealing with Notes Receivable. For one thing, there’s always the risk that the borrower may default on their loan or go bankrupt before paying back the note in full. Assume if are notes receivable a current asset RSP was unable to pay the final installment of USD20,000 and the related interest of USD165 and MPC has been accruing this interest income. Now the note has been completely discharged, MPC has recorded an interest income of USD987.
- This may involve detailing past due or impaired notes, as well as the movements in the allowance for credit losses.
- 11 Financial’s website is limited to the dissemination of general information pertaining to its advisory services, together with access to additional investment-related information, publications, and links.
- While accounts receivable represent amounts owed by customers for goods or services provided on credit, notes receivable are formal agreements where the borrower promises to repay a specific amount by a certain date.
- Notes receivable is the written document that the customers make to agree to pay a specific amount on a specific date.
- It distinguishes between amounts expected to be realized within the next operating cycle (current assets) and those not expected to be realized within that timeframe (noncurrent assets).
Create a Free Account and Ask Any Financial Question
- These types of notes can help businesses manage cash flow and provide short-term financing solutions.
- Typically, notes receivable are expected to be collected within one year, making them different from accounts receivable.
- The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) in the United States, through the Accounting Standards Codification (ASC), provides guidance on the recognition of notes receivable, typically under ASC 310 on receivables.
- DEF, Inc., another client of PQR, Inc. issued a 2-month promissory note against their outstanding balance of $3 million on 1 November 20X4.
Still, if the amount is not expected to receive within a year or an operating cycle then it is treated as non-current assets in the balance sheet. Just as was the case with accounts receivable, there is a possibility that the holder of the note receivable will not be able to collect some or all of the amounts owing. When the investment in a note receivable becomes impaired for any reason, the receivable is re-measured at the present value of the currently expected cash flows at the loan’s original effective interest https://www.bookstime.com/ rate. Notes receivable can arise due to loans, advances to employees, or from higher-risk customers who need to extend the payment period of an outstanding account receivable. Notes can also be used for sales of property, plant, and equipment or for exchanges of long-term assets.
Interest Rate
- Interest receivable on the note as a 31 December is reported as current asset because it is to be received at the end of April 20X5.
- Below is the schedule for the interest and amortization calculations using the effective interest method.
- Interest receivable is recognized on the balance sheet in addition to the face value of notes receivable.
- The terms of the note receivable state that the customer must repay the principal amount of $10,000 plus interest accrued at 8% per year by the maturity date of January 1, 2024.
- Note receivable is the better option because there is a very high chance of getting payment on time with the note receivable as compared to the simple credit transaction.
Notes receivable come in the form of a written document that borrowers pay to their lenders. Unlike usual trading balances and credits, notes receivable balances come with additional terms. Additionally, managing and tracking multiple notes receivable can be time-consuming and require resources that smaller companies don’t have readily available. Notes receivable may not be suitable for every type of business since they tie up capital and may limit flexibility during times when liquidity becomes important. After 60 days of non-payment, notes payable are issued to MPC by RSP Co. for USD60,000 at an interest rate of 10% per annum and with a payment of USD20,000 due at the end of each of the next 90 days. This adjusting journal entry is needed to conform to GAAP, recording revenue in the month it is earned.

The implied interest rate is calculated to be 5% and the note’s interest component (rounded) is $2,165 (), which is the difference between the cash lent and the higher amount of cash repaid at maturity. Below is the schedule for the interest and amortization calculations using the effective interest method. Interest on a note receivable is calculated by multiplying the principal balance of the note by the interest rate and by the number of days that have elapsed since the last interest payment was made divided by 365. The journal entry for interest on a note receivable is to debit the interest income account and credit the cash account. There are several elements of promissory notes that are important to a full understanding of accounting for these notes. These are the note’s principal, maturity date, duration, interest rate, and maturity value.